When statins alone aren’t enough to lower LDL-C, consider NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL1,2
NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL are the only nonstatins FDA approved to lower LDL-C and reduce the risk of MI and coronary revascularization in primary prevention and secondary prevention patients.1,2
Significant 38% mean LDL-C reduction vs placebo at Week 121
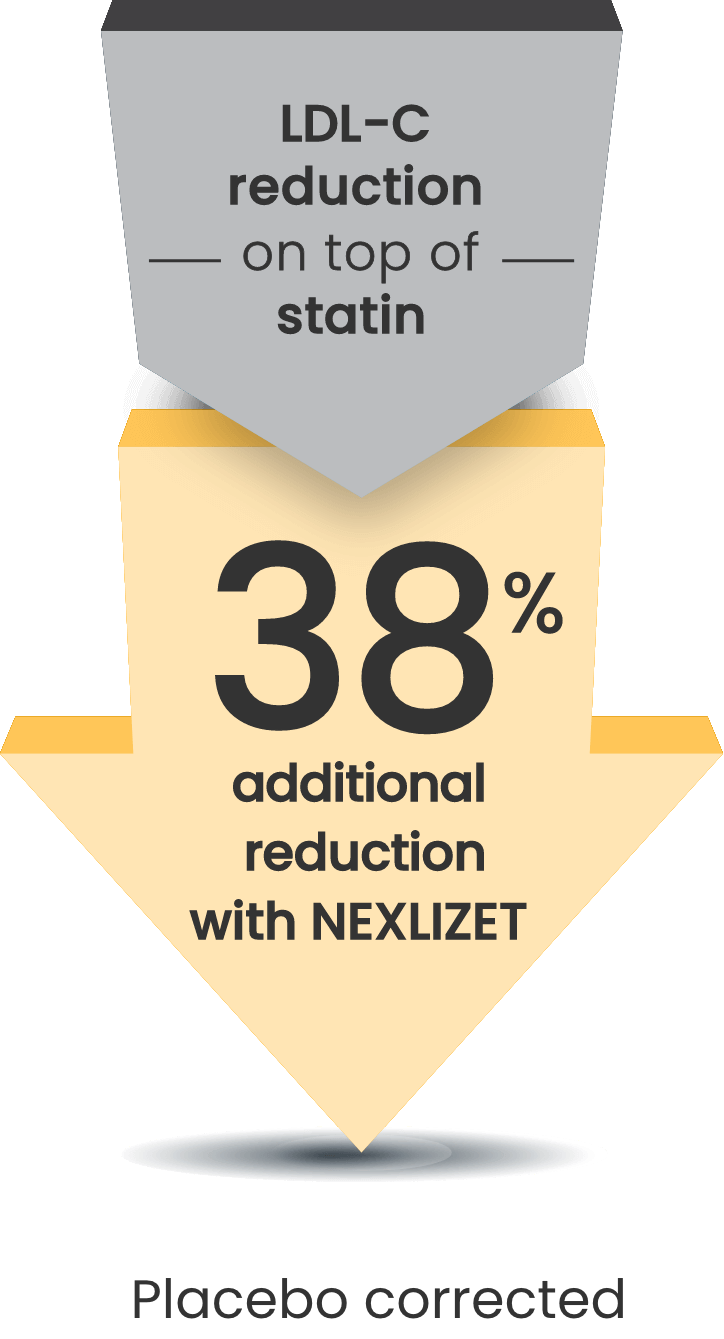
LDL-C changes from baseline at Week 12 (LS mean; P<0.001)1:
- NEXLIZET: -36% (n=86)
- Placebo: +2% (n=41)
Consistent efficacy has been observed across a range of statin intensities1,3:
- 65% of patients were on a statin; 35% were on a high-intensity dose
Maximum
When statins alone aren’t enough, NEXLETOL significantly reduces LDL-C2
CLEAR Harmony: LDL-C changes from baseline at Week 12
(LS mean; P<0.001)2:
- NEXLETOL: -17% (n=1488)
- Placebo: +2% (n=742)
CLEAR Wisdom: LDL-C changes from baseline at Week 12
(LS mean; P<0.001)2:
- NEXLETOL: -15% (n=522)
- Placebo: +2% (n=257)
baseline to Week 122


Interested in samples?
Get patients started with a 14-day sample of NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL.
Request samplesINDICATION AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Indication
NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL are indicated:
- The bempedoic acid component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction and coronary revascularization in adults who are unable to take recommended statin therapy (including those not taking a statin) with:
- established cardiovascular disease (CVD), or
- at high risk for a CVD event but without established CVD.
- As an adjunct to diet:
- NEXLIZET, alone or in combination with other LDL-C lowering therapies, to reduce LDL-C in adults with primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH.
- NEXLETOL, in combination with other LDL-C lowering therapies, or alone when concomitant LDL-C lowering therapy is not possible, to reduce LDL-C in adults with primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL are contraindicated in patients with a prior hypersensitivity to bempedoic acid or ezetimibe or any of the excipients. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria have been reported.
Hyperuricemia : Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, may increase blood uric acid levels, which may lead to gout. Hyperuricemia may occur early in treatment and persist throughout treatment, returning to baseline following discontinuation of treatment. Assess uric acid levels periodically as clinically indicated. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia, and initiate treatment with
Tendon Rupture : Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, is associated with an increased risk of tendon rupture or injury. Tendon rupture may occur more frequently in patients over 60 years of age, in those taking corticosteroid or fluoroquinolone drugs, in patients with renal failure, and in patients with previous tendon disorders. Discontinue NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL at the first sign of tendon rupture. Consider alternative therapy in patients who have a history of tendon disorders or tendon rupture.
The most common adverse reactions in the primary hyperlipidemia trials of bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, in ≥2% of patients and greater than placebo were upper respiratory tract infection, muscle spasms, hyperuricemia, back pain, abdominal pain or discomfort, bronchitis, pain in extremity, anemia, and elevated liver enzymes.
Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ezetimibe (a component of NEXLIZET) and at an incidence greater than placebo in clinical trials were upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, arthralgia, sinusitis, pain in extremity, fatigue, and influenza.
In the primary hyperlipidemia trials of NEXLIZET, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥3% and greater than placebo) observed with NEXLIZET, but not observed in clinical trials of bempedoic acid or ezetimibe, were urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and constipation.
The most common adverse reactions in the cardiovascular outcomes trial for bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, at an incidence of ≥2% and 0.5% greater than placebo were hyperuricemia, renal impairment, anemia, elevated liver enzymes, muscle spasms, gout, and cholelithiasis.
Concomitant use of NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL with greater than 20 mg of simvastatin or 40 mg of pravastatin should be avoided due to the potential for increased risk of simvastatin- or pravastatin-related myopathy.
Discontinue NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL when pregnancy is recognized unless the benefits of therapy outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breast-fed infant, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL.
Report pregnancies to Esperion Therapeutics, Inc. Adverse Event reporting line at at 1-833-377-7633.
Please see full Prescribing Information for NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL.
INDICATION AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Indication
NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL are indicated:
- The bempedoic acid component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction and coronary revascularization in adults who are unable to take recommended statin therapy (including those not taking a statin) with:
- established cardiovascular disease (CVD), or
- at high risk for a CVD event but without established CVD.
- As an adjunct to diet:
- NEXLIZET, alone or in combination with other LDL-C lowering therapies, to reduce LDL-C in adults with primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH.
- NEXLETOL, in combination with other LDL-C lowering therapies, or alone when concomitant LDL-C lowering therapy is not possible, to reduce LDL-C in adults with primary hyperlipidemia, including HeFH.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL are contraindicated in patients with a prior hypersensitivity to bempedoic acid or ezetimibe or any of the excipients. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria have been reported.
Hyperuricemia : Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, may increase blood uric acid levels, which may lead to gout. Hyperuricemia may occur early in treatment and persist throughout treatment, returning to baseline following discontinuation of treatment. Assess uric acid levels periodically as clinically indicated. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia, and initiate treatment with
Tendon Rupture : Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, is associated with an increased risk of tendon rupture or injury. Tendon rupture may occur more frequently in patients over 60 years of age, in those taking corticosteroid or fluoroquinolone drugs, in patients with renal failure, and in patients with previous tendon disorders. Discontinue NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL at the first sign of tendon rupture. Consider alternative therapy in patients who have a history of tendon disorders or tendon rupture.
The most common adverse reactions in the primary hyperlipidemia trials of bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, in ≥2% of patients and greater than placebo were upper respiratory tract infection, muscle spasms, hyperuricemia, back pain, abdominal pain or discomfort, bronchitis, pain in extremity, anemia, and elevated liver enzymes.
Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ezetimibe (a component of NEXLIZET) and at an incidence greater than placebo in clinical trials were upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, arthralgia, sinusitis, pain in extremity, fatigue, and influenza.
In the primary hyperlipidemia trials of NEXLIZET, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥3% and greater than placebo) observed with NEXLIZET, but not observed in clinical trials of bempedoic acid or ezetimibe, were urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and constipation.
The most common adverse reactions in the cardiovascular outcomes trial for bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL, at an incidence of ≥2% and 0.5% greater than placebo were hyperuricemia, renal impairment, anemia, elevated liver enzymes, muscle spasms, gout, and cholelithiasis.
Concomitant use of NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL with greater than 20 mg of simvastatin or 40 mg of pravastatin should be avoided due to the potential for increased risk of simvastatin- or pravastatin-related myopathy.
Discontinue NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL when pregnancy is recognized unless the benefits of therapy outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breast-fed infant, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with NEXLIZET or NEXLETOL.
Report pregnancies to Esperion Therapeutics, Inc. Adverse Event reporting line at at 1-833-377-7633.
Please see full Prescribing Information for NEXLIZET and NEXLETOL.
HeFH=heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia; hsCRP=high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; LDL-C=low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LS=least squares; MI=myocardial infarction; non-HDL-C=non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; total C=total cholesterol.
REFERENCES
1. NEXLIZET. Prescribing information. Esperion Therapeutics, Inc.; 2024. 2. NEXLETOL. Prescribing information. Esperion Therapeutics, Inc.; 2024. 3. Ballantyne CM, Laufs U, Ray KK, et al. Bempedoic acid plus ezetimibe fixed-dose combination in patients with hypercholesterolemia and high CVD risk treated with maximally tolerated statin therapy. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2020;27(6):593–603. 4. Ray KK, Bays HE, Catapano AL, et al. Safety and efficacy of bempedoic acid to reduce LDL cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(11):1022-1032. 5. Goldberg AC, Leiter LA, Stroes ESG, et al. Effect of bempedoic acid vs placebo added to maximally tolerated statins on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease: the CLEAR Wisdom randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322(18):1780-1788.